Reducing/Shrinking a logical volume is a high risk of data corruption, so try to avoid this situation as much as possible. But, sometimes we may need to do it if there are no other options.
It is always recommended to take a backup before shrinking an LVM partition. If it’s a SAN disk, take a snapshot, it’s very easy to restore.
If you are new to Logical Volume Management (LVM), I recommend reading the LVM series article listed below:
Make a Note: Shrinking is not supported in GFS2 and XFS file system.
- Part-1: How to Create/Configure LVM (Logical Volume Management) in Linux
- Part-2: How to Extend/Increase LVM’s (Logical Volume Resize) in Linux
- Part-3: How to Reduce/Shrink LVM’s (Logical Volume Resize) in Linux
- Part-4: How to Remove Physical Volume from a Volume Group in LVM
- Part-5: How to Remove LVM (Logical) Volume in Linux
- Part-6: How to recover deleted Logical volume (LV) in LVM
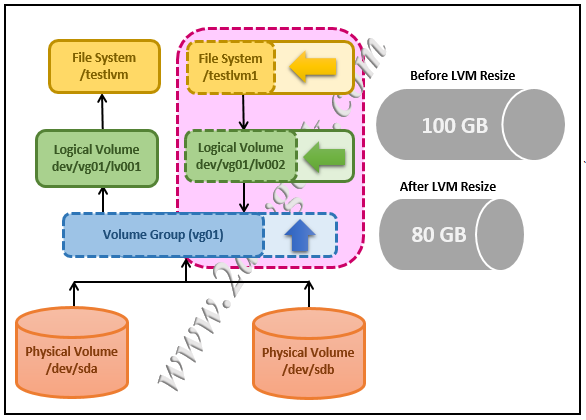
Reducing the logical volume involves the below steps.
- Unmount the file system.
- Check the file system for any errors.
- Shrink the file system size.
- Reduce the logical volume size.
- Re-check the file system for errors (Optional).
- Mount the file system
- Check the reduced file system size
For instance: You have a 100GB logical volume that is not using the entire volume for storing data, so you decide to reduce it to 80GB and use the remaining 20GB for other purposes. To do so, follow the below procedure.
# df -h /testlvm1 Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 100G 15G 85G 12% /testlvm1
1) Unmounting the file system
Use the umount command to unmount the file system.
# umount /testlvm1
2) Check the file system for any Errors
Check the file system for any errors using the e2fsck command.
# e2fsck -f /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 e2fsck 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013) Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizes Pass 2: Checking directory structure Pass 3: Checking directory connectivity Pass 4: Checking reference counts Pass 5: Checking group summary information /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002: 13/6553600 files (0.0% non-contiguous), 12231854/26212352 blocks
3) Shrinking a File System
The resize2fs command is used to enlarge or shrink ext2, ext3 and ext4 file systems on a device. It can be used to enlarge a mounted file system, but to shrink it, you must unmount the file system.
The below command will reduce the "testlvm1" file system from 100GB to 80GB.
Common syntax for file system resize
Syntax:
resize2fs [Path_of_LV] [New file system size]
The actual command is as follows.
# resize2fs /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 80G resize2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013) Resizing the filesystem on /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 to 28321400 (4k) blocks. The filesystem on /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 is now 28321400 blocks long.
4) Reducing a Logical Volume (LVM)
Now reduce the logical volume size using the lvreduce command. The below command "/dev/mapper/vg01-lv002" will shrink the Logical volume from 100GB to 80GB.
Common syntax for LVM Reduce (lvreduce)
Syntax:
lvreduce [New LV Size] [Path_of_LV]
The actual command is as follows.
# lvreduce -L 80G /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 WARNING: Reducing active logical volume to 80.00 GiB THIS MAY DESTROY YOUR DATA (filesystem etc.) Do you really want to reduce lv002? [y/n]: y Reducing logical volume lv002 to 80.00 GiB Logical volume lv002 successfully resized
5) Optional: Check the file system for any Errors
Check the file system again if there are any errors after LV has been reduced.
# e2fsck -f /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 e2fsck 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013) Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizes Pass 2: Checking directory structure Pass 3: Checking directory connectivity Pass 4: Checking reference counts Pass 5: Checking group summary information /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002: 13/4853600 files (0.0% non-contiguous), 1023185/2021235 blocks
6) Mounting a file system
Finally mount the file system and check the reduced file system size.
Use the mount command to mount the logical volume.
# mount /testlvm1
Check the newly mounted volume using the df command.
# df -h /testlvm1 Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/mapper/vg01-lv002 80G 15G 65G 18% /testlvm1
Final Thoughts
I hope you have learned how to Shrink a File System and Logical Volume (LVM) in this article. This can be achieved in five easy steps.
If you have any questions or feedback, feel free to comment below.




One Comment on “How to Reduce LVM Partition Size in Linux”