Most people use wireless networks as their primary source to access the internet.
You may need to monitor your wireless internet speed when you experience a slowness in connectivity or when fluctuating between fast and slow network speeds.
Linux operating systems have a variety of tools for manipulating and monitoring the wireless networks.
In this article, we will explain you how to view the available WiFi networks, bit rate, link quality, signal strength, etc, on Linux from the command line.
Multiple tools are used to obtain WiFi information on Linux, but we will show you only the best tools among them.
1) Checking wireless card chipset information
‘lspci’ command is used to display information about PCI buses in the system and devices connected to them.
Run the following command to identify your wireless network card manufacturer name:
$ sudo lspci | grep -i wireless 08:00.0 Network controller: Intel Corporation Wireless 8260 (rev 3a)
To check wireless card driver information, use the following command:
$ sudo lspci -vv -s 08:00.0 | grep -i 'kernel'
Kernel driver in use: iwlwifi
Kernel modules: iwlwifi
WiFi driver and firmware version information can be found using the ethtool command as shown below:
$ sudo ethtool -i wlan0 driver: iwlwifi version: 5.3.18-lp152.66-default firmware-version: 36.77d01142.0 expansion-rom-version: bus-info: 0000:08:00.0 supports-statistics: yes supports-test: no supports-eeprom-access: no supports-register-dump: no supports-priv-flags: no
2) Identifying wireless interface name in Linux
ip command is used to check the network interface name, their associated IP address, MAC address and other information.
Wired & Wireless network interfaces can be identified using the first letter of their name, as shown below:
- e – Wired network interface
- w – Wireless network interface
$ ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enp9s0: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether c8:5b:76:4d:d4:5c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
3: wlp8s0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state up group default qlen 1000
link/ether e4:a7:a0:32:fc:e9 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.4/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute wlp8s0
valid_lft 83000sec preferred_lft 83000sec
inet6 fe80::ad00:2f7e:d882:5add/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
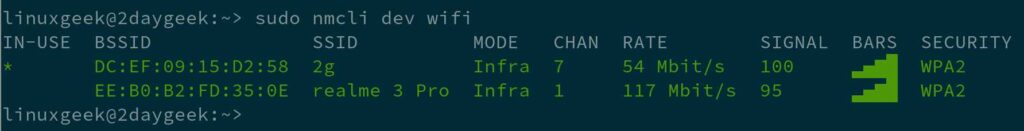
3) Scan and list available WiFi networks using nmcli command
‘nmcli’ is a command-line tool for controlling NetworkManager and reporting network status. It is used to create, display, edit, delete, activate, and deactivate network connections, as well as control and display network device status.
Run the following command to see the available wireless networks’ SSID, mode, channel, transfer rate, signal strength, bars and security.
- (*) – Indicates that your computer is currently connected to this WiFi network.
To see detailed information for “2g” WiFi connection, run:
$ nmcli connection show 2g
To view detailed information only about ‘general & wifi-properties’ of “vlan0” (WiFi) interface, run:
$ nmcli -f GENERAL,WIFI-PROPERTIES dev show vlan0 GENERAL.DEVICE: wlan0 GENERAL.TYPE: wifi GENERAL.NM-TYPE: NMDeviceWifi GENERAL.DBUS-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/Devices/3 GENERAL.VENDOR: Intel Corporation GENERAL.PRODUCT: Wireless 8260 GENERAL.DRIVER: iwlwifi GENERAL.DRIVER-VERSION: 5.3.18-lp152.66-default GENERAL.FIRMWARE-VERSION: 36.77d01142.0 GENERAL.HWADDR: E4:A7:A0:32:FC:E9 GENERAL.MTU: 1500 GENERAL.STATE: 100 (connected) GENERAL.REASON: 0 (No reason given) GENERAL.IP4-CONNECTIVITY: 4 (full) GENERAL.IP6-CONNECTIVITY: 3 (limited) GENERAL.UDI: /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.2/0000:08:00.0/net/wlan0 GENERAL.IP-IFACE: wlan0 GENERAL.IS-SOFTWARE: no GENERAL.NM-MANAGED: yes GENERAL.AUTOCONNECT: yes GENERAL.FIRMWARE-MISSING: no GENERAL.NM-PLUGIN-MISSING: no GENERAL.PHYS-PORT-ID: -- GENERAL.CONNECTION: 2g GENERAL.CON-UUID: ac068067-c5b6-4fae-a361-e1b4d42d1060 GENERAL.CON-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/2 GENERAL.METERED: no (guessed) WIFI-PROPERTIES.WEP: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.WPA: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.WPA2: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.TKIP: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.CCMP: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.AP: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.ADHOC: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.2GHZ: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.5GHZ: yes WIFI-PROPERTIES.MESH: no WIFI-PROPERTIES.IBSS-RSN: yes
4) Checking wireless network (WiFi) & card information using iwconfig command
Iwconfig is similar to ifconfig, but is dedicated to the wireless interfaces. It is used to set the parameters of the network interface which are specific to the wireless operation.
Iwconfig may also be used to display those parameters, and the wireless statistics (extracted from /proc/net/wireless).
All these parameters and statistics are device dependent. Each driver will provide only some of them depending on hardware support, and the range of values may change. Please refer to the man page of each device for details.
From the following output, you can find, wireless card supported transfer rate, link quality, signal strenth, etc,.
$ sudo iwconfig wlan0
wlan0 IEEE 802.11 ESSID:"2g"
Mode:Managed Frequency:2.442 GHz Access Point: DC:EF:09:15:D2:58
Bit Rate=54 Mb/s Tx-Power=22 dBm
Retry short limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Encryption key:off
Power Management:off
Link Quality=65/70 Signal level=-45 dBm
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:188 Missed beacon:0
5) Checking wireless interface information using iwlist command
‘Iwlist’ is used to display some additional information from a wireless network interface compared to iwconfig including wifi quality and wifi signal strength or level.
$ sudo iwlist wlan0 scan
wlan0 Scan completed :
Cell 01 - Address: DC:EF:09:15:D2:58
Channel:7
Frequency:2.442 GHz (Channel 7)
Quality=70/70 Signal level=-39 dBm
Encryption key:on
ESSID:"2g"
Bit Rates:1 Mb/s; 2 Mb/s; 5.5 Mb/s; 11 Mb/s; 9 Mb/s
18 Mb/s; 36 Mb/s; 54 Mb/s
Bit Rates:6 Mb/s; 12 Mb/s; 24 Mb/s; 48 Mb/s
Mode:Master
Extra:tsf=0000000f54595a11
Extra: Last beacon: 52ms ago
IE: Unknown: 00023267
IE: Unknown: 010882848B961224486C
IE: Unknown: 030107
IE: Unknown: 2A0100
IE: Unknown: 32040C183060
IE: IEEE 802.11i/WPA2 Version 1
Group Cipher : CCMP
Pairwise Ciphers (1) : CCMP
Authentication Suites (1) : PSK
IE: Unknown: DD180050F2020101000003A4000027A4000042435E0062322F00
IE: Unknown: 0B05030006127A
IE: Unknown: DD07000C4304000000
IE: Unknown: DDA90050F204104A0001101044000102103B00010310470010388330923092188382D5DCEF0915D2581021000D4E4554474541522C20496E632E1023001D4E45544745415220576972656C6573732041636365737320506F696E74102400074E4554474541521042000831323334353637381054000800060050F204000110110014574E523631342028576972656C6573732041502910080002210C103C0001011049000600372A000120
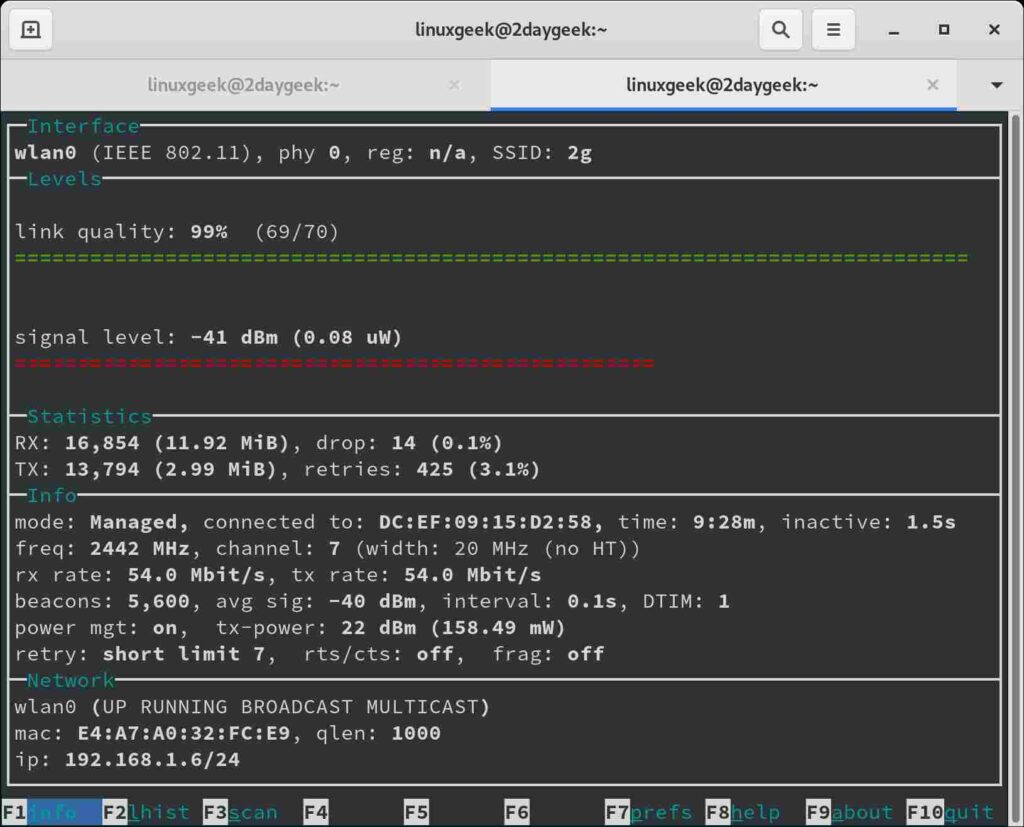
6) Checking wireless interface information using wavemon command?
‘wavemon‘ is a ncurses-based monitoring application for wireless network devices. It plots levels in real-time as well as showing wireless and network related device information.
The ‘wavemon’ interface splits into different “screens” and each screen contains different information:
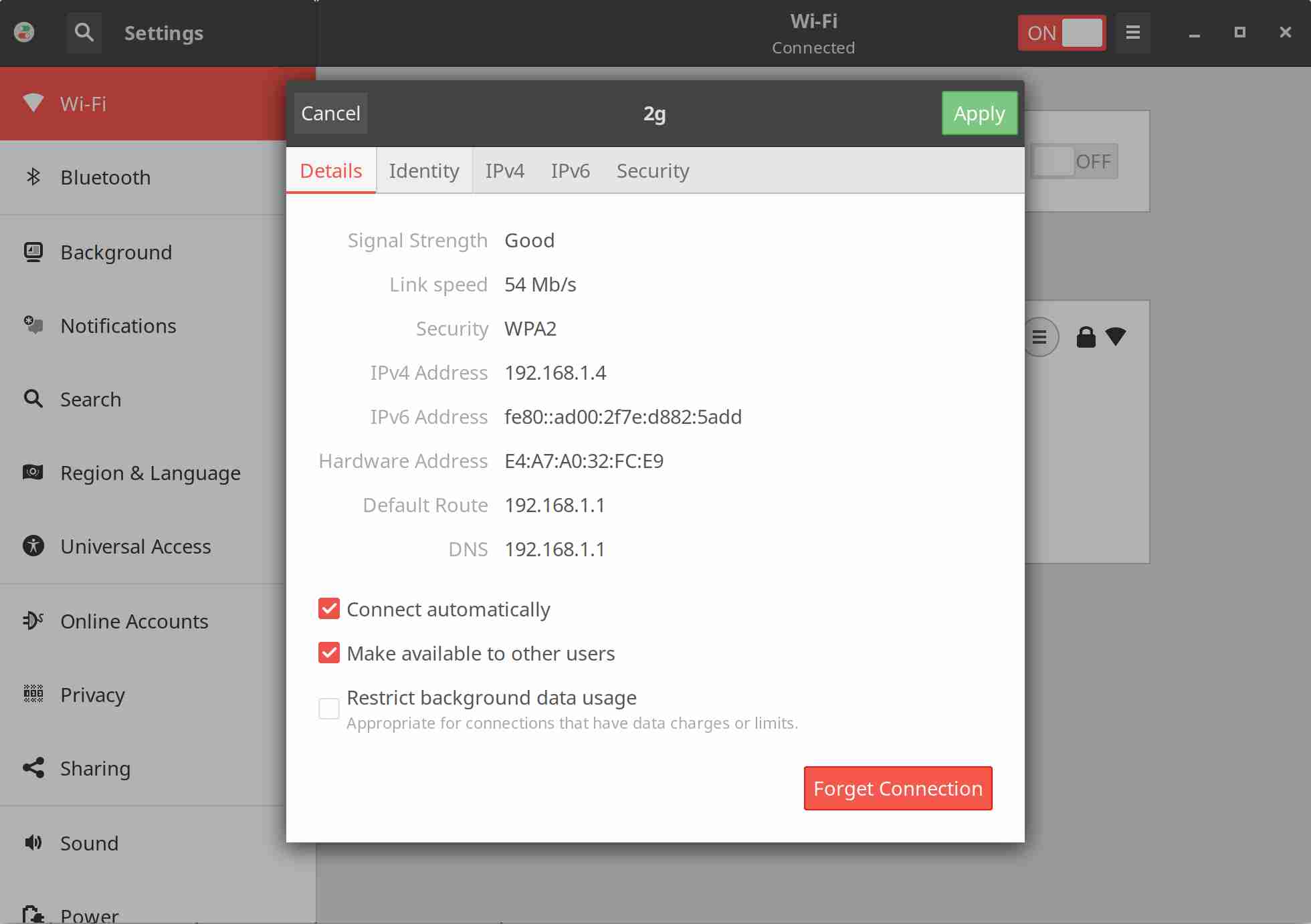
7) Check Wifi information using GNOME NetworkManager command?
The NetworkManager daemon attempts to make networking configuration and operation as painless and automatic as possible by managing the primary network connection and other network interfaces, like Ethernet, WiFi, and Mobile Broadband devices.
NetworkManager will connect any network device when a connection for that device becomes available, unless that behavior is disabled. Information about networking is exported via a D-Bus interface to any interested application, providing a rich API with which to inspect and control network settings and operation.
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial, we have shown you several commands to check wireless network information such as available WiFi networks, bit rate, link quality, signal strength, etc, on Linux from the command line.
If you found this article helpful, please do share with your friends and spread the knowledge. Please feel free to comment below if you have any queries/concerns. We will get back to you as soon as we can. Happy learning!



Great tips! Thank you for the article.