In servers, Network interfaces either physical or virtual can be enabled or disabled by running some commands.
If any change is performed in NIC due to which the interface is down, the interface can be brought up through multiple ways but we would like to suggest six best methods as mentioned below:
Commands as follows:
- ifconfig command: ifconfig command is used to configure a network interface. It provides a lot of information about NIC.
- ifdown/ifup Command: ifdown command bring the network interface down whereas the ifup command brings the network interface up.
- ip Command: ip command is used to manage NIC. It is a replacement of old and deprecated ifconfig command. It is similar to ifconfig command but has many powerful features which is not available with ifconfig command.
- nmcli Command: nmcli is a command-line tool for controlling Network Manager and to report network status.
- systemctl command: systemctl command is a tool which is responsible for controlling the systemd system and service manager.
- nmtui Command: nmtui is a curses‐based TUI application for interacting with Network Manager.
ip command shows the available network interface card information in the Linux system. According to the below output, two network interfaces (enp0s3 & enp0s8) are up and running in the system.
# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:c2:e4:e8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.4/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp0s3
valid_lft 86049sec preferred_lft 86049sec
inet6 fe80::3899:270f:ae38:b433/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: enp0s8: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:30:5d:52 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.3/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp0s8
valid_lft 86049sec preferred_lft 86049sec
inet6 fe80::32b7:8727:bdf2:2f3/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
1) Bring UP/Down Network Interface, using ifconfig command
ifconfig runs at boot time to set up network interfaces and provides a lot of information about the NIC. In this example, let us see, how to bring up and down the interface using ifconfig command.
Common Syntax for ifconfig:
# ifconfig [NIC_NAME] Down/Up
Run the following command to bring down the enp0s3 interface in the system. Please remember to enter the interface name of your system, instead of “enp0s3” as mentioned in this example.
# ifconfig enp0s3 down
As per the following output, enp0s3 interface is down
# ip a sh dev enp0s3 2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state DOWN group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:c2:e4:e8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Please run the following command to bring up the enp0s3 interface.
# ifconfig enp0s3 up
“enp0s3” interface status can be further verified by running the following command.
# ip a sh dev enp0s3 2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000 link/ether 08:00:27:c2:e4:e8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff inet 192.168.1.4/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp0s3 valid_lft 86294sec preferred_lft 86294sec inet6 fe80::3899:270f:ae38:b433/64 scope link noprefixroute valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2) How to enable and disable Network Interface using ifdown/ifup command?
‘ifdown’ command brings the Network interface down whereas the ‘ifup’ command bring the Network interface up.
Note: These commands does not work on new interface device bearing the names enpXXX.
Common Syntax for ifdown/ifup:
# ifdown [NIC_NAME] # ifup [NIC_NAME]
Run the following command to bring down the eth1 interface.
# ifdown eth1
Run the following command to check, if the eth1 interface is down.
# ip a sh dev eth1
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state DOWN qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:d5:a0:18 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Run the following command to bring up the eth1 interface.
# ifup eth1
“eth1” interface status can be further verified by running the following command.
# ip a sh dev eth1
3: eth1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:d5:a0:18 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.7/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global eth1
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fed5:a018/64 scope link tentative dadfailed
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
As mentioned earlier, ifup and ifdown does not support the latest interface device bearing the names such as enpXXX. Unknown interface message will appear when executed.
# ifdown enp0s8 Unknown interface enp0s8
3) Bringing UP/Down Network Interface using ip command?
In this example, let us discuss how to bring Up/Down the Network interface using ip command.
Common Syntax for ip:
# ip link set Down/Up
Run the following command to bring down the enp0s3 interface.
# ip link set enp0s3 down
enp0s3 interface is down, as per the following output.
# ip a sh dev enp0s3
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:c2:e4:e8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Run the following command to bring up the enp0s3 interface.
# ip link set enp0s3 up
“enp0s3” interface status can be further verified by running the following command.
# ip a sh dev enp0s3
2: enp0s3: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 08:00:27:c2:e4:e8 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.1.4/24 brd 192.168.1.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute enp0s3
valid_lft 86294sec preferred_lft 86294sec
inet6 fe80::3899:270f:ae38:b433/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
4) How to enable & disable Network Interface using nmcli command?
nmcli command can be used as a replacement for nm-applet or other graphical clients. nmcli is used to create, display, edit, delete, activate and deactivate network connections, as well as control and display network device status.
nmcli command performs most of the task using profile name instead of device name. Run the following command to identify the interface names.
# nmcli con show NAME UUID TYPE DEVICE Wired connection 1 3d5afa0a-419a-3d1a-93e6-889ce9c6a18c ethernet enp0s3 Wired connection 2 a22154b7-4cc4-3756-9d8d-da5a4318e146 ethernet enp0s8
Common Syntax for nmcli:
# nmcli con Down/Up
As stated, enter the profile name instead of device name to bring down the interface. Run the following command to bring down the enp0s3 interface.
# nmcli con down 'Wired connection 1' Connection 'Wired connection 1' successfully deactivated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/6)
According to the below output, enp0s3 interface is down.
# nmcli dev status DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION enp0s8 ethernet connected Wired connection 2 enp0s3 ethernet disconnected -- lo loopback unmanaged --
Run the following command to bring up the enp0s3 interface.
# nmcli con up 'Wired connection 1' Connection successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/7)
Now the enp0s3 interface is up.
# nmcli dev status DEVICE TYPE STATE CONNECTION enp0s8 ethernet connected Wired connection 2 enp0s3 ethernet connected Wired connection 1 lo loopback unmanaged --
5) Bringing UP/Down Network Interface using systemctl command?
The ‘systemctl’ command can be used to apply a new configuration for the network service which brings down and brings up all the Network Interface Cards (NICs) to load the new configuration.
# systemctl restart network or # systemctl restart network.service
6) Bringing UP/Down Network Interface using nmtui tool?
nmtui is a curses based TUI application used for interacting with Network Manager.
It allows us to easily configure the network interfaces on Linux system using GUI.
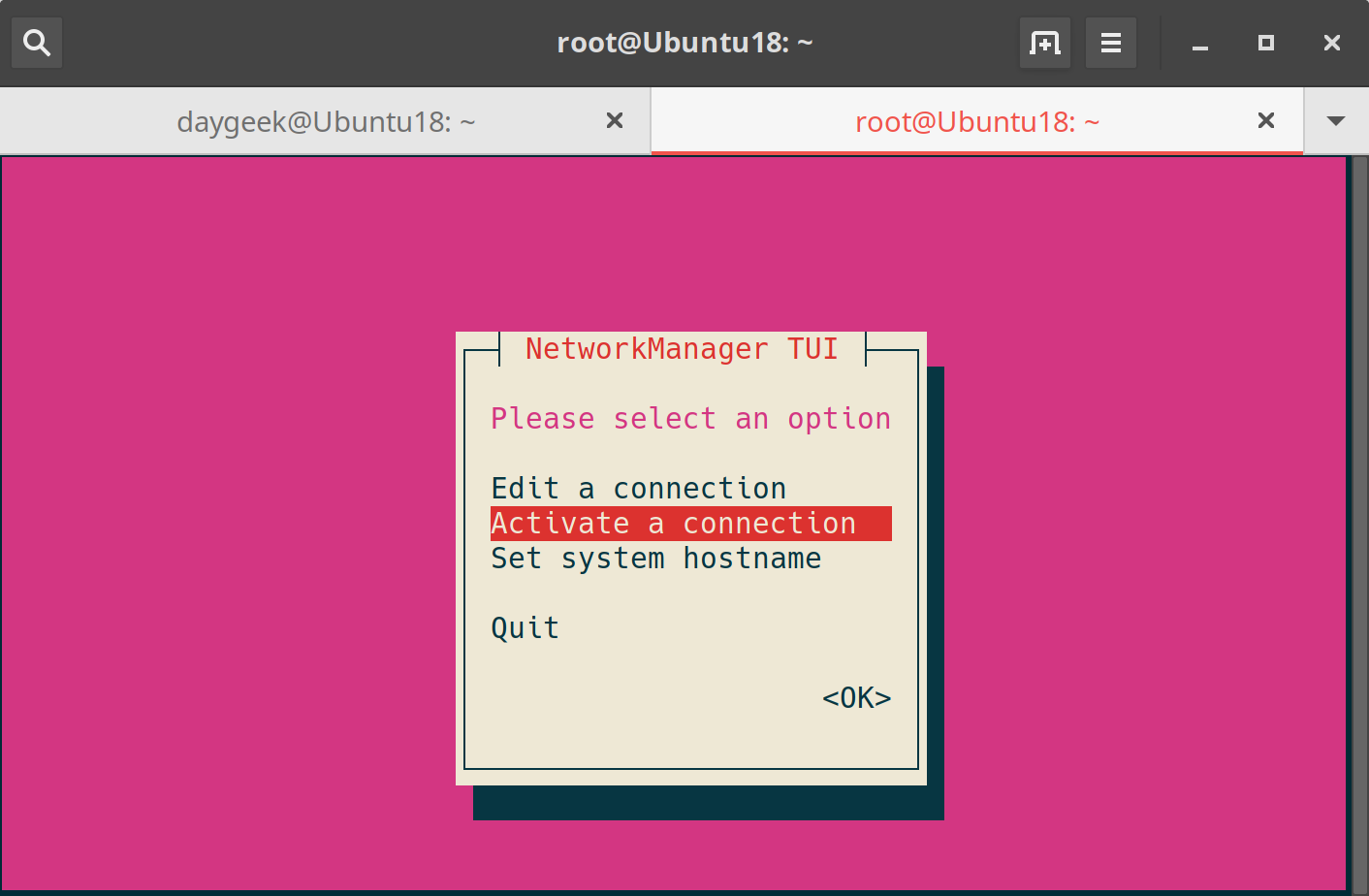
Run the following command to launch the nmtui interface. Select “Activate a connection” and hit “OK”
# nmtui
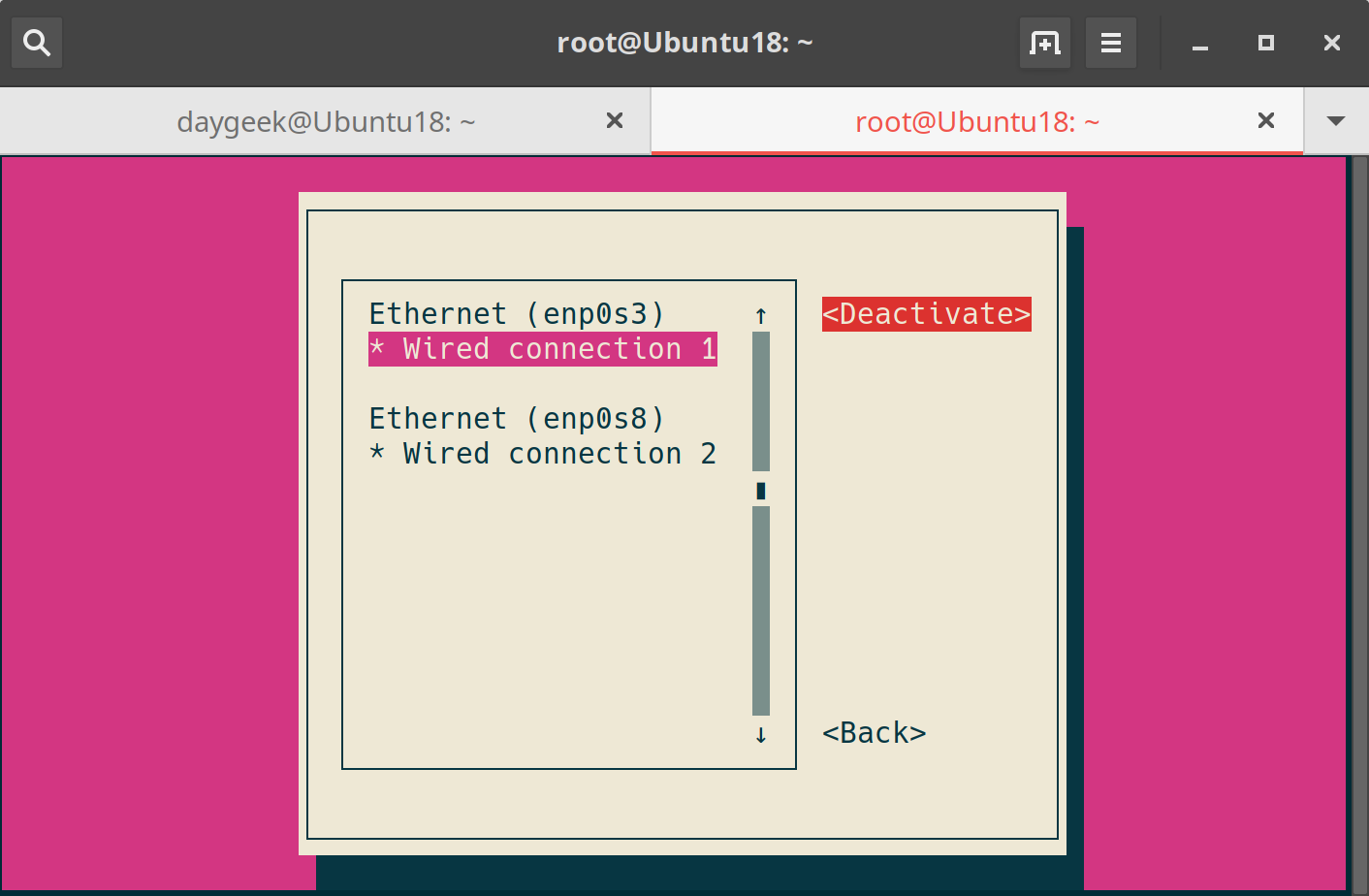
Select the desired interface to bring down and then hit “Deactivate” button.
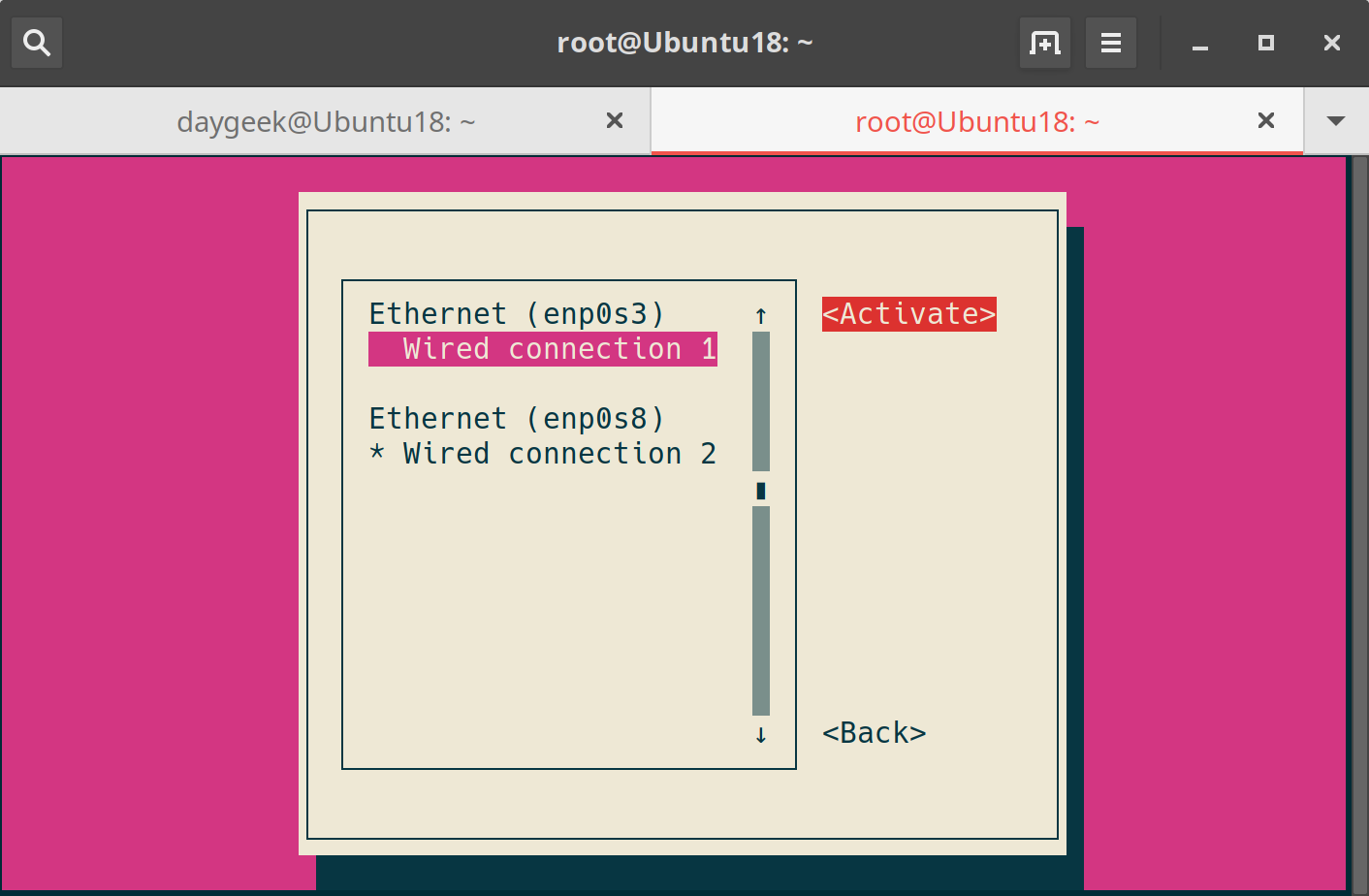
For activation, please perform the same procedure as above.




I would recommend to use :
# ip a sh dev eth1
in stead of :
# ip a | grep -A 5 “eth1:”
@Bockor, Thanks, it has been updated as suggested.
And you can also do the following:
# systemctl network-manager.service
@ROMSAT, Thanks, yes, we can use # systemctl restart network.service, which brings down and brings up all the Network Interface Cards (NICs) to load the new configuration. Will add the same in the article