A hostname (also known as a Computer Name) is a name which is given to a device (It could be a system, switch, router, etc) that is connected to the network, and is used to identify it over a network. There cannot be two systems with same host names within the same network.
The purpose of assigning names to IP addresses is to make them easier for people to remember. In reality, an IP address identifies a network interface associated with a device like a network card.
Refer the following articles on how to change a hostname in Linux:
By default, the hostname can be found in the terminal, but it only shows the first part when the hostname is large (each hostname usually has at least one numeric network address associated with it).
In this tutorial, we will show you how to check hostname using several ways in Linux.
- hostnamectl Command: hostnamectl command is controling the system hostname.
- nmcli Command: nmcli is a command-line tool for controlling NetworkManager.
- uname Command: Print certain system information.
- hostname: Show or set system host name.
- sysctl: sysctl command allows us to configure kernel parameters at runtime.
1) Checking HostName using hostnamectl command
hostnamectl may be used to query and change the system hostname and related settings. Run the hostnamectl command to view the system hostname as shown below:
$ hostnamectl
or
$ hostnamectl status
Static hostname: daygeek-Y700
Icon name: computer-laptop
Chassis: laptop
Machine ID: 31bdeb7b83230a2025d43547368d75bc
Boot ID: 267f264c448f000ea5aed47263c6de7f
Operating System: Manjaro Linux
Kernel: Linux 4.19.20-1-MANJARO
Architecture: x86-64
2) Checking the Linux system hostname
Hostname is the program that is used to either set or display the current host, domain or node name of the system. These names are used by many of the networking programs to identify the machine. The domain name is also used by NIS/YP.
$ hostname daygeek-Y700
3) Checking HostName with uname command
uname (stands for unix name) is a utility that prints the system information like name, version and other details about the system, and the operating system running on it:
$ uname -a | awk '{print $2}'
CentOS.2daygeek.com
4) Checking HostName using nmcli command
nmcli is a command-line tool for controlling NetworkManager and reporting network status.
nmcli is used to create, display, edit, delete, activate, and deactivate network connections, as well as control and display network device status. Also, it allow us to view the hostname.
Use the following format to view the current hostname using nmcli :
$ nmcli general hostname daygeek-Y700
5) Checking HostName using sysctl command
‘sysctl’ is used to modify kernel parameters at runtime. The parameters available are those listed under /proc/sys/. Procfs is required for sysctl support in Linux. You can use sysctl to both read and write sysctl data.
$ sysctl kernel.hostname kernel.hostname = daygeek-Y700
Bonus Tips:
Alternatively, you can use the following commands to verify the hostname in Linux. These are additional methods but I rather recommend using the aforementioned five commands as they are most widely used.
- nmtui Command: nmtui is a text User Interface for controlling NetworkManager.
- /etc/hostname file: This file is containing the static system hostname.
- /etc/hosts: /etc/hosts file is an operating system file that maps hostnames to IP addresses.
- /etc/sysconfig/network: The /etc/sysconfig/network file specifies additional information that is valid to all network interfaces on the system.
- /proc/sys/kernel/hostname: The proc filesystem (procfs) is a special filesystem in Unix-like operating systems.
Method-1: Check HostName using /etc/hostname file
Alternatively, we can view the hostname by using the /etc/hostname file.
Check the current hostname using /etc/hostname file.
$ cat /etc/hostname daygeek-Y700
Method-2: Check HostName using /etc/hosts file
‘/etc/hosts’ file is an operating system file that maps hostnames to IP addresses before DNS can be referenced. It is a plain text file, one line per IP address. It’s a static table lookup for hostnames as shown below:
$ cat /etc/hosts | grep daygeek 127.0.1.1 daygeek-Y700
Method-3: Check HostName using ProcFS in Linux
The proc filesystem (procfs) is a special filesystem in Unix-like operating systems that presents information about processes and other system information.
It’s sometimes referred to as a process information pseudo-file system. It doesn’t contain ‘real’ files but runtime system information (e.g. system memory, devices mounted, hardware configuration, etc).
$ cat /proc/sys/kernel/hostname daygeek-Y700
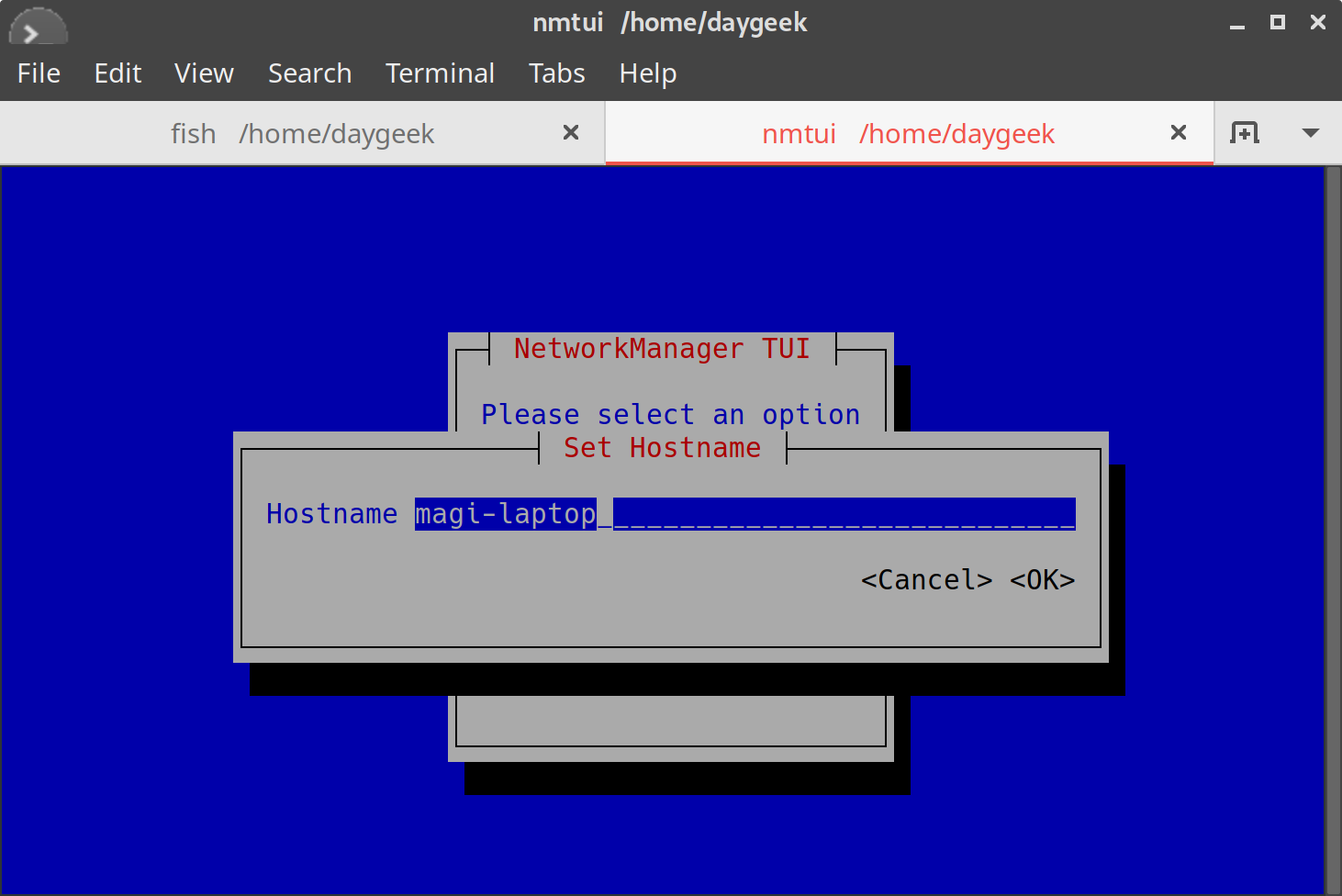
Method-4: View HostName with nmtui
nmtui is a curses‐based TUI application for interacting with NetworkManager. When starting nmtui, the user is prompted to choose the activity to perform unless it was specified as the first argument.
Run the following command on terminal to launch the terminal user interface:
$ nmtui
Method-5: Check HostName using /etc/sysconfig/network file
The ‘/etc/sysconfig/network’ file specifies additional information that is valid to all network interfaces on the system.
For RHEL/CentOS 6 systems only:
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/network | grep -i hostname HOSTNAME=CentOS.2daygeek.com
Wrapping Up
In this tutorial we’ve shown you ten commands to check the hostname in Linux.
If you found this article helpful, please do share with your friends and spread the knowledge. Please feel free to comment below if you have any queries/concerns. We will get back to you as soon as we can. Happy learning!